Hyper Text Markup Language
HTML is the foundation of every website and an essential skill for anyone learning web design. In this guide, you’ll explore the basics of HTML forms, input types, and attributes that make web pages interactive and user-friendly
Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages
- HTML describes the structure of a Web page
- HTML consists of a series of elements
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML elements label pieces of content such as “this is a heading”, “this is a paragraph”, “this is a link”, etc.
Example
<!DOCTYPLE html>
<html>
<head>
<title > Basic Layout of HTML code</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My first Heading</h1>
<p>My Paragraph of the web page </p>
</body>
</html>
Example Explained
The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document
The <html> element is the root element of an HTML page
The <head> element contains meta-information about the HTML page
The <title> element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser’s title bar or the page’s tab)
The <body> element defines the document’s body and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc.
The <h1> element defines a large heading
The <p> element defines a paragraph
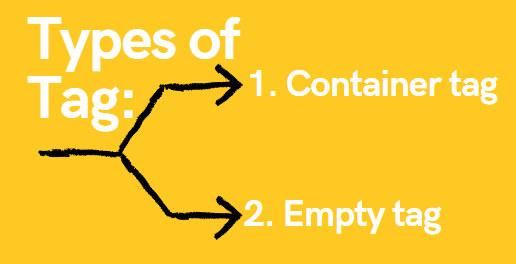
What are Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML) Element?
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag:
<tagname> Content goes here… </tagname>
Example Explained
These are the tag which has two parts , one is opening tag and other is closing tag, which takes the following from.
Ex: <tag> XXXXXXXXXX </tag>
Empty tags are the tags that don’t need to close. These tags are placed where needed.
a. <br> (line break) break rule
b. <hr> horizontal rule
Note: HTML is a case-insensitive type language, which means you can type HTML code in any case such as uppercase, lowercase, and capitalized code, but make sure both the opening tags are written in the same case.
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them correctly.
A browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
Web Browsers
How to use HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language) using NotePad or TextEdit.
- Web pages can be created and modified by using professional HTML editors.
- However, for learning HTML we recommend a simple text editor like Notepad (PC) or TextEdit (Mac).
- We believe that using a simple text editor is a good way to learn HTML.
- Follow the steps below to create your first web page with Notepad or TextEdit.
Notepad
Open the Start Screen (the window symbol at the bottom left on your screen). Type Notepad.
Or with Windows 7 or earlier:
Open Start > Programs > Accessories > Notepad
Write or copy the following HTML code into Notepad:
Save the file on your computer. Select File > Save as in the Notepad menu.
Name the file “index.html” and set the encoding to UTF-8 (which is the preferred encoding for HTML files).
Open the saved HTML file in your favorite browser (double-click on the file, or right-click – and choose “Open with”).
The result will look much like this:
TextEdit
Open Finder > Applications > TextEdit
Also change some preferences to get the application to save files correctly. In Preferences > Format > choose “Plain Text”
Then under “Open and Save”, check the box that says “Display HTML files as HTML code instead of formatted text”.
Then open a new document to place the code.
Want to join?
Looking for a teacher you can truly learn from? Join me online or face-to-face, where clarity, guidance, and results come first
Formatting Tags
Formatting tags are used to make some text on the webpage to appear differently than normal text.
Tags
<b></b>→ Makes text bold (stylistic, no extra meaning).<i></i>→ Makes text italic (stylistic, no extra meaning).<s></s>→ Shows text with astrikethrough(used for content that’s no longer accurate or relevant).<u></u>→ <u>Underlines</u> text (stylistic).<sub></sub>→ Displays text as subscript (below baseline, e.g., H<sub>2</sub>O).<sup></sup>→ Displays text as superscript (above baseline, e.g., x<sup>2</sup>).<tt></tt>→ Old/obsolete tag for monospaced text. Use<code>or CSS instead.<q></q>→ Adds inline quotation marks around text (e.g., “quoted text”).<mark></mark>→ <mark>Highlights text</mark> with a background color (default is yellow).
In short:
Some are stylistic only (
<b>, <i>, <u>, <s>).Some are for notation (
<sub>, <sup>).Some add meaning (
<q>, <mark>).One is obsolete (
<tt>).

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Formatting Tags Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>Bold:</b> This is <b>bold text</b>.</p>
<p><i>Italic:</i> This is <i>italic text</i>.</p>
<p><s>Strikethrough:</s> This is <s>strikethrough text</s>.</p>
<p><u>Underline:</u> This is <u>underlined text</u>.</p>
<p><sub>Subscript:</sub> H<sub>2</sub>O</p>
<p><sup>Superscript:</sup> x<sup>2</sup> + y<sup>2</sup></p>
<p><tt>Monospaced (obsolete):</tt> <tt>Monospaced text</tt></p>
<p><q>Quotation:</q> He said, <q>Hello World!</q></p>
<p><mark>Highlight:</mark> This is <mark>highlighted text</mark>.</p>
</body>
</html>
Heading Tag
HTML headings are titles or subtitles that you want to display on a webpage.
HTML headings are defined with <h1> to <h6> tags.
- <h1>Learn HTML with Zailearn.com</h1>
- <h2>Learn HTML with Zailearn.com</h2>
- <h3>Learn HTML with Zailearn.com</h3>
- <h4>Learn HTML with Zailearn.com</h4>
- <h5>Learn HTML with Zailearn.com</h5>
- <h6>Learn HTML with Zailearn.com</h6>
Paragraph Tag
HTML paragraphs are defined with <p> </p>tag.
<p>Learn HTML with ZaiLearn and build a strong foundation in web design, step by step.</p>
Body Tag
The <body> tag encloses all the tags, attributes and information to be displayed in the web page.
Attributes
1. bgcolor
2. text
3. background
Bgcolor
Text
Background
If image and HTML file in different location
HTML Media
🖼️ Image in HTML
The HTML <img> element is used to display images on a webpage.
Unlike <video> or <audio>, the <img> tag is self-closing (it doesn’t need a closing tag).
Basic Example
<img src=”photo.jpg” alt=”A beautiful sunset” width=”400″ height=”300″>
How It Works
src→ The file path or URL of the image.alt→ Alternative text (shows when the image can’t load, also helps with SEO & accessibility).width&height→ Control the size of the image (in px or %).
Common Attributes of <img>
src="file.jpg"→ Path of the image file.alt="description"→ Text shown if image doesn’t load.width="300"/height="200"→ Image size.title="info text"→ Tooltip when mouse hovers.align="left/right/middle"(obsolete, use CSS) → Aligns image.border="2"(obsolete, use CSS) → Adds border around image.
Basic image
<img src=”logo.png” alt=”Website Logo” width=”150″>
Image from a URL
<img src=”https://example.com/image.jpg” alt=”Online Image” width=”300″>
Note:
🎬 Video in HTML
The HTML <video> element is used to show videos on a webpage.
Basic Example
<video width=”320″ height=”240″ controls>
<source src=”movie.mp4″ type=“video/mp4”>
<source src=”movie.ogg” type=”video/ogg”>
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>
How It Works
controls→ Adds buttons like play, pause, volume.width&height→ Fix video size. (If not set, the page may flicker while loading.)<source>→ Lets you add multiple formats (e.g.,.mp4,.ogg). The browser will play the first one it supports.Fallback text → The text inside
<video> ... </video>shows up only in browsers that don’t support<video>.
Autoplay & Muted
You can make videos play automatically using autoplay.
👉 But most browsers only allow autoplay if the video is muted.
Example with autoplay + muted:
<video width=”320″ height=”240″ autoplay muted>
<source src=”movie.mp4″ type=”video/mp4″>
<source src=”movie.ogg” type=”video/ogg”>
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>
Common Attributes of <video>
controls→ Shows play, pause, volume buttons.autoplay→ Starts video automatically.muted→ Starts video without sound.loop→ Repeats the video automatically.poster="image.jpg"→ Shows an image before the video starts.
🎵 Audio in HTML
The HTML <audio> element is used to play sound files (like music or voice) on a webpage.
Basic Example
<audio controls>
<source src=”song.mp3″ type=”audio/mpeg”>
<source src=”song.ogg” type=”audio/ogg”>
Your browser does not support the audio element.
</audio>
How It Works
controls→ Adds play, pause, volume, and timeline buttons.<source>→ Lets you add multiple audio formats (e.g.,.mp3,.ogg). The browser will play the first one it supports.Fallback text → The text between
<audio> ... </audio>shows up only in browsers that don’t support<audio>.
Common Attributes of
controls→ Shows play, pause, volume controls.autoplay→ Starts playing automatically (often requiresmuted).loop→ Repeats the audio automatically.muted→ Starts audio without sound.preload="auto/metadata/none"→ Tells the browser how to load the file:auto→ Load whole audio when page loadsmetadata→ Load only details (length, etc.)none→ Don’t load until the user clicks play
Autoplay + Loop
<audio autoplay loop>
<source src=”song.mp3″ type=”audio/mpeg”>
<source src=”song.ogg” type=”audio/ogg”>
</audio>
Autoplay + Muted (required on many browsers)
<audio autoplay muted>
<source src=”song.mp3″ type=”audio/mpeg”>
</audio>
In short for students:
Use
<audio>for sound.Always add
controlsso users can play/pause.Use
autoplay,loop,mutedto control behavior.Add multiple formats for better browser support.
Font Tag
The font tag is used to style the content of the webpage.
Attributes
- Face
- Size
- color
Face
The font face attribute is used to apply font styles on text.
Syntax: <font face= “Font_style_name”>Some content here</font>
Example: <font face= “Lucida Calligraphy”>Website</font>
Size
The font size attribute is used to change the size of the text. The size can be given in numeric from 1 to 7.
Syntax: <font size= size>Some content here</font>
Example: <font size= 5>This is text</font>
Color
The font color attribute is used to give color to the content.
Syntax: <font color= “color_name”>Some content here</font>
Example: <font color= “red”>This is text</font>
List
Unordered List
This type of list represent points symbols such as
- Disc (By default)
- Circle
- Square
Tag: — <ul></ul>
List elements : — <li></li>
Type : Type is an attribute which is used to change the points of list and it is used for both ordered list and unordered list.
<ul type= “circle”></ul>
Example
<ul>
<li> this is Zailearn</li>
<li> this is Zailearn</li>
<li> this is Zailearn</li>
</ul>
Ordered List
This type of list represent points in sequence or order such as Commonly used attributes of <ol> </ol> tags :
- Type-it is use to define the type of numbering format. Syntax : type= “number”
- Start : it is use to define the starting point of numbering into the list .
Syntax : start= “starting number”· 1,2,3 …· A,B,C,…..· a,b,c,….· I,II,III,IV,…..· i,ii,iii,…..
Tag: — <ol>…..</ol>
List element: — <li>….</li>
Type : Type is an attribute which is used to change the points of list and it is used for both ordered list and unordered list.
<ol type= “A”></ol>
Example
<ol>
<li> this is Zailearn</li>
<li> this is Zailearn</li>
<li> this is Zailearn</li>
</ol>
Table in HTML
The table in HTML is created using the <table></table> tag.
Everything inside a table must be written between these two tags.
Common Table Sub-Tags:
<caption>...</caption>→ Table title or name<tr>...</tr>→ Table row<th>...</th>→ Table header (bold, centered by default)<td>...</td>→ Table data cell
Attributes of table Tag
Attributes are used to style and control the appearance of tables.
width→ Defines table width — <table width=“60%”>height→ Defines table height — <table height=“200”>border→ Adds border around table — <table border=“2”>bordercolor→ Sets color of table border — <table border=“2” bordercolor=“green”>bgcolor→ Adds background color to table, row, or cell — <table bgcolor=“lightblue”><tr bgcolor="yellow">
<td bgcolor="pink">cellspacing→ Space between cells — <table cellspacing=“10”>cellpadding→ Space inside a cell (between content & border) —<table cellpadding=“10”>align→ Aligns table (left, right, center) — <table align=“center”>
Attributes for or
Colspan → Merge multiple columns into one
<th colspan="3">Merged Column</th>
Rowspan → Merge multiple rows into one
<td rowspan="2">Merged Row</td>
📋 HTML Forms
Forms in HTML allow users to enter data that can be sent to a web server.
They are created using the <form>...</form> element.
The <form> Tag
<form> … form elements … </form>
Everything inside <form> is part of the form.
The data entered by the user can be submitted to a server for processing.
1. Input
Used to collect different kinds of user input.
Examples: text box, checkbox, radio button, password, etc.
<input type="text"> <!-- Single line text box -->
<input type="password"> <!-- Password field -->
<input type="checkbox"> <!-- Multiple selection -->
<input type="radio"> <!-- Single selection -->
<input type="submit"> <!-- Submit button -->
<input type="button" value="Click Me"> <!-- Normal button -->
2. Textarea
For multi-line text input.
Attributes:
rows → Number of text rows
cols → Number of text columns
<textarea rows="4" cols="30"></textarea>
3. Select
Creates a drop-down list.
<select>
<option value="html">HTML</option>
<option value="css">CSS</option>
<option value="js">JavaScript</option>
</select>
Input Types in HTML
Here are different input types you can use:
<input type=”button”>
<input type=”checkbox”>
<input type=”color”>
<input type=”date”>
<input type=”datetime-local”>
<input type=”email”>
<input type=”file”>
<input type=”hidden”>
<input type=”image”>
<input type=”month”>
<input type=”number”>
<input type=”password”>
<input type=”radio”>
<input type=”range”>
<input type=”reset”>
<input type=”search”>
<input type=”submit”>
<input type=”tel”>
<input type=”text”>
<input type=”time”>
<input type=”url”>
<input type=”week”>
Want to join?
Looking for a teacher you can truly learn from? Join me online or face-to-face, where clarity, guidance, and results come first
Scroll to Top
Colspan→ Merge multiple columns into one<th colspan="3">Merged Column</th>
Rowspan→ Merge multiple rows into one<td rowspan="2">Merged Row</td>
📋 HTML Forms
Forms in HTML allow users to enter data that can be sent to a web server.
They are created using the <form>...</form> element.
The <form> Tag
<form> … form elements … </form>
Everything inside <form> is part of the form.
The data entered by the user can be submitted to a server for processing.
1. Input
Used to collect different kinds of user input.
Examples: text box, checkbox, radio button, password, etc.
<input type="text"> <!-- Single line text box -->
<input type="password"> <!-- Password field -->
<input type="checkbox"> <!-- Multiple selection -->
<input type="radio"> <!-- Single selection -->
<input type="submit"> <!-- Submit button -->
<input type="button" value="Click Me"> <!-- Normal button -->2. Textarea
For multi-line text input.
Attributes:
rows→ Number of text rowscols→ Number of text columns
<textarea rows="4" cols="30"></textarea>3. Select
Creates a drop-down list.
<select>
<option value="html">HTML</option>
<option value="css">CSS</option>
<option value="js">JavaScript</option>
</select>
Input Types in HTML
Here are different input types you can use:
<input type=”button”>
<input type=”checkbox”>
<input type=”color”>
<input type=”date”>
<input type=”datetime-local”>
<input type=”email”>
<input type=”file”>
<input type=”hidden”>
<input type=”image”>
<input type=”month”>
<input type=”number”>
<input type=”password”>
<input type=”radio”>
<input type=”range”>
<input type=”reset”>
<input type=”search”>
<input type=”submit”>
<input type=”tel”>
<input type=”text”>
<input type=”time”>
<input type=”url”>
<input type=”week”>
Want to join?
Looking for a teacher you can truly learn from? Join me online or face-to-face, where clarity, guidance, and results come first







